Biofilm DL Segmentation
Background
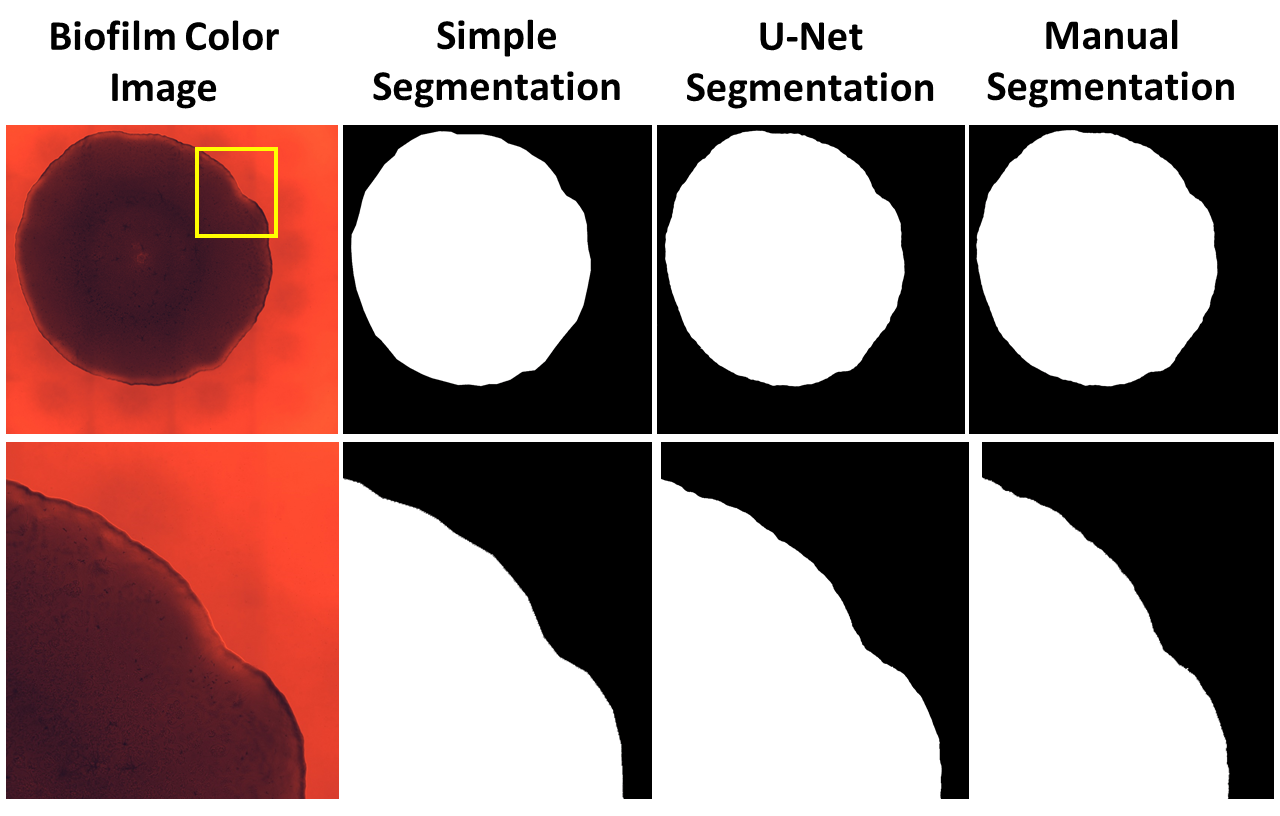
As part of a final project for BMI567: Medical Image Analysis taught by Daniel Pimental-Alarcon in 2020, I applied U-net deep learning segmentation to segment bacteria biofilm images. These images were extremely large, making training and manual segmentation (ground-truth) very difficult. To add to this, some biofilms consisted of very rough edges, which made accurate segmentation quite difficult. The abstract for the final paper is provided below:
Accurate segmentation is important for quantifying structural and temporal characteristics of biofilm cultures and is of particular importance when monitoring a biofilm’s response to antibiotic treatment regimens. However, the large size of microscopy images, as well as the large number of images that may be needed for proper cell-tracking over multiple biofilm strains, warrant automated means of segmentation to expedite post-processing and increase segmentation repeatability. In this study, a fully convolutional neural network with U-Net architecture was trained to segment Pseudomonas Aeruginosa biofilm images using a total of 60 training and 10 validation datasets. This deep learning approach was compared to a “simple” manual segmentation using multi-vertex polygon ROI tracing. Both methods were compared to ground-truth biofilm images and quantitatively assessed using dice coefficients and modified Hausdorff distances to rate the efficacy of each method. Ground-truth images were obtained by producing an approximate mask using various morphological operations and by extensive manual fine-tuning of edges. Intra-observer repeatability of simple segmentation and ground-truth segmentation was assessed for 10 repeat datasets using intraclass correlation coefficients. It was found that ground-truth manual segmentation was extremely time-consuming, taking on average 23 minutes while simple segmentation took on average 1 minute. Deep learning segmentation resulted in fairly low accuracy, as measured by dice coefficients and Hausdorff distances. Further studies utilizing different frameworks, better computational resources, and augmented datasets are warranted to provide increased accuracy of automatic deep learning segmentation of biofilm images.

Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *